Step-by-Step Guide to Creating Snapshots of Virtual Machines in vSphere
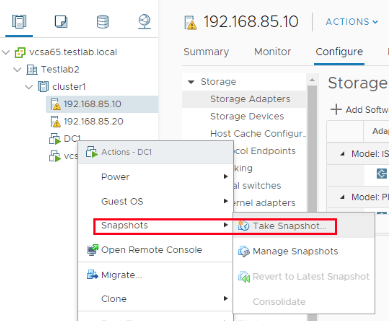
Table of Contents
Introduction
VMware vSphere snapshots are a critical feature for maintaining virtual machine (VM) stability and flexibility. These snapshots capture the state of a VM at a specific moment, including its disk, memory, and power settings. This functionality makes snapshots essential for various tasks, such as testing, troubleshooting, backups, and disaster recovery.
In this guide, we’ll provide a detailed explanation of VMware snapshots, their components, and their importance. We’ll also walk through step-by-step instructions to create and manage snapshots in vSphere, followed by a lab tutorial to apply the concepts in a real-world scenario.
What is a Snapshot in VMware vSphere?
A snapshot in VMware vSphere is a checkpoint that preserves the current state of a VM, including its:
- Disk State: Captures the data on the VM’s virtual disk (VMDK) at the moment of the snapshot. Any subsequent changes are saved in a delta disk file.
- Memory State (Optional): Saves the contents of the VM’s RAM, allowing it to resume from the exact point it was paused.
- Power State: Records whether the VM was powered on, off, or suspended at the time the snapshot was taken.
Snapshots are a versatile tool, ensuring administrators can revert a VM to its prior state when needed, making them invaluable for managing virtualized environments.
Why Use Snapshots in VMware vSphere?
Snapshots offer multiple benefits, including:
Safe Testing Environment
Ideal for testing software updates, patches, or configuration changes. If issues arise, administrators can revert the VM to its previous state.
Reliable Backup Integration
Snapshots provide a temporary checkpoint during backups, ensuring data consistency.
Troubleshooting Aid
Snapshots help diagnose issues without permanent changes to the VM.
Application Testing
Multi-tier applications can be captured and tested as a group, ensuring easier debugging and optimization.
How Snapshots Work in VMware vSphere
Snapshots use a layered disk structure:
- Base Disk: The primary virtual disk remains unchanged after the snapshot.
- Delta Disk: Stores all changes made after the snapshot. The VM writes to this file instead of the base disk.
If memory is included in the snapshot, the VM’s RAM contents are also saved, enabling a seamless restoration of the running state.
When a snapshot is deleted, changes in the delta disk are merged back into the base disk to ensure the VM reflects its latest state.
Step-by-Step Guide: How to Create a Snapshot in VMware vSphere
Steps
Access vSphere
Log in to the vSphere Client.
Select the VM
Navigate to the VM Inventory and choose the VM you want to snapshot.
Initiate Snapshot Creation
Right-click the VM > Snapshots > Take Snapshot.
Configure Snapshot Options
Provide a name and description. Choose whether to include the VM’s memory state.
Validate Snapshot Creation
Go to the Snapshots Tab under the VM and ensure the snapshot is listed.
Perform Changes
Make a change to the VM (e.g., update software or modify files).
Revert to Snapshot
Right-click the VM > Snapshots > Revert to Snapshot.
Delete the Snapshot
Select the snapshot > Click Delete All to remove it from the system.
Limitations of Snapshots
Snapshots in VMware vSphere are a valuable tool for protecting virtual machines (VMs) and providing recovery options. there are some important limitations and considerations to keep in mind when using snapshots.
When a snapshot is created, it captures the state of the VM, including its disk, memory, and configuration. Any changes to the VM after the snapshot are written to a delta disk. This can lead to performance degradation, especially if the snapshot is kept for a long time. The more snapshots you accumulate, the more disk space and resources are required, which may impact VM performance.
The snapshot files (delta disks) grow over time as changes are made to the VM. If the VM is active and constantly changing, the snapshot disk can grow large, potentially consuming significant storage space.
If you clone a VM with active snapshots, the cloned VM will carry the snapshots over. This can lead to complications if the snapshots are not removed properly after cloning.
Conclusion
VMware vSphere snapshots are indispensable for ensuring control over VM states and operations. By capturing precise states of VMs, administrators can safeguard against potential disruptions and ensure smooth recovery during testing, backups, and troubleshooting. With this comprehensive understanding of snapshots and the practical lab tutorial, you’re equipped to manage snapshots effectively in your virtualized environment.








Well written and interesting. Nicely done.