Understanding Amazon Elastic Compute Cloud (EC2)

In today’s fast-paced digital landscape, businesses need powerful, scalable computing resources to run their applications efficiently. Managing physical servers, however, can be costly and complex. That’s where cloud computing steps in—offering a more flexible, cost-effective alternative. At the heart of this transformation is Amazon Elastic Compute Cloud (EC2), a key service from Amazon Web Services (AWS).
In this blog post, we’ll take a closer look at Amazon EC2, exploring its core features, benefits, and practical use cases. Whether you’re a cloud beginner or an experienced developer, understanding EC2 will help you deploy applications with ease and agility. By delivering virtual machines on-demand, EC2 lets you scale as needed and focus on growing your business—while AWS manages the infrastructure behind the scenes.
Get ready to dive in and unlock the full potential of Amazon EC2!
Understanding Amazon EC2
The term “EC2” stands for Elastic Cloud Compute. When you request an EC2 instance from AWS, you are essentially asking for a virtual server that combines CPU, RAM, and disk resources. AWS provisions a virtual machine for you, allowing you to use a shared physical server’s resources efficiently.
VMware Cloud Foundation Platform
Why Use Amazon EC2?
One of the key advantages of using EC2 instances is the ability to offload maintenance tasks to AWS. Instead of managing server upgrades, security patches, and uptime monitoring, AWS takes care of these tasks for you. Additionally, using EC2 instances on AWS is cost-effective, as you only pay for the resources you use, and you can easily scale up or down based on your needs.
Types of Amazon EC2 Instances
Amazon EC2 offers a diverse range of instance types, each optimized for specific workloads. Understanding these types is crucial for selecting the instance that best suits your application’s needs, ensuring optimal performance and cost-efficiency.
Here’s a breakdown of some common EC2 instance categories:
- General Purpose: These instances provide a balanced mix of compute, memory, and storage resources, making them suitable for various applications like web servers, development environments, and small databases.
- Compute Optimized: Prioritize raw processing power, ideal for computationally intensive workloads like scientific simulations, high-performance computing (HPC), and video processing.
- Memory Optimized: Offer generous memory capacity, catering to applications requiring in-memory databases, large-scale data processing, and memory-intensive workloads.
- Storage Optimized: Designed for applications demanding significant storage capacity and I/O throughput, such as big data analytics, data warehousing, and log processing.
- Accelerated Computing: Integrate hardware accelerators like GPUs and FPGAs, ideal for workloads requiring intensive graphics processing, machine learning, and video encoding/decoding.
By carefully considering your application’s resource requirements, you can select the optimal EC2 instance type, maximizing performance while keeping costs under control.
Regions and Availability Zones
AWS has data centers located across the world, known as regions. Within each region, there are multiple availability zones, which provide redundancy and fault tolerance. By selecting the appropriate region and availability zone, you can optimize latency and ensure high availability for your applications.
Creating an Amazon EC2 Instance
The AWS Management Console provides a user-friendly interface for launching EC2 instances, essentially creating your virtual server in the cloud. Here’s a simplified overview of the process:
VMware Cloud Foundation Platform
- Navigate to the EC2 service: Access the EC2 dashboard within the AWS Management Console. Log in to AWS Management Console and choose EC2.
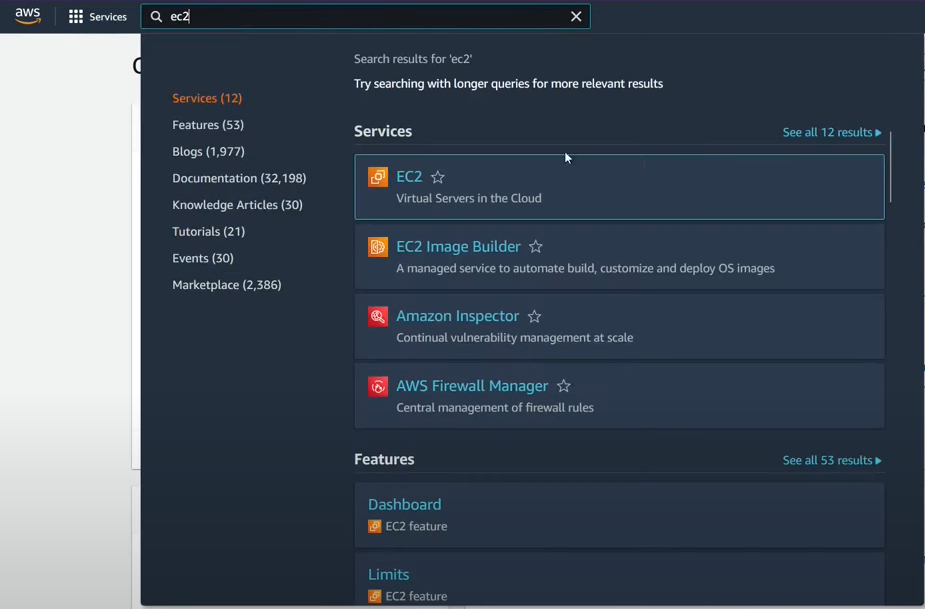
Choose your instance type: Select the appropriate instance type based on your application’s resource needs. In our case, we’ll choose t2.micro.
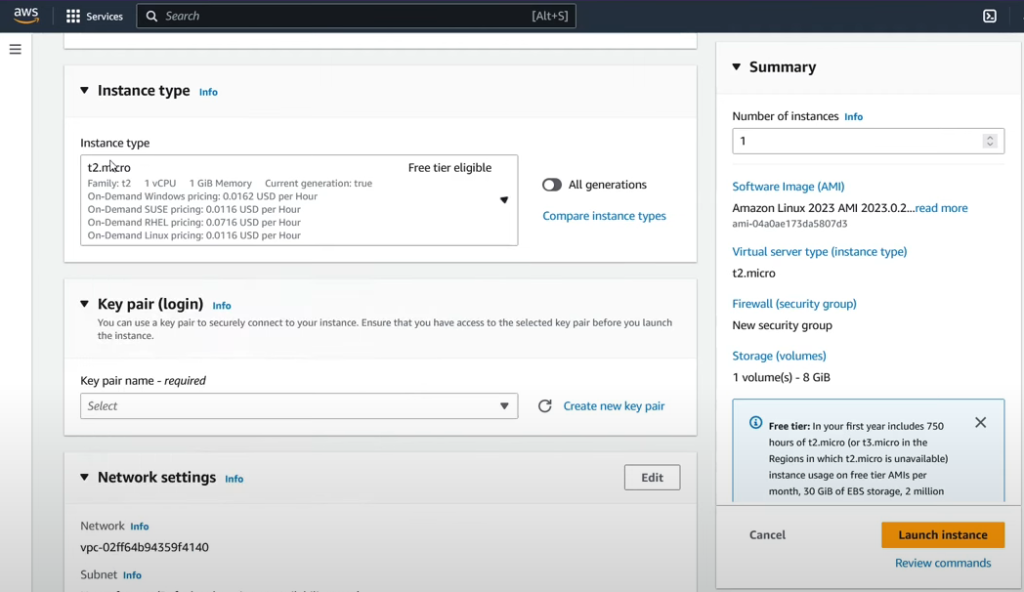
Pick an operating system: Decide on the desired operating system for your instance, such as Windows or Linux distributions.
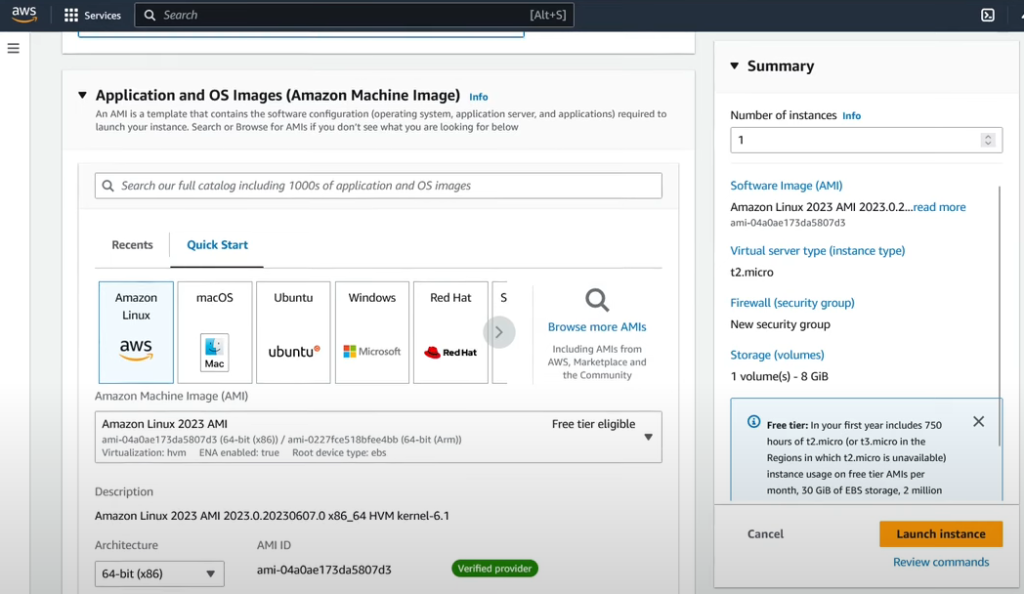
Configure key pair and settings: Generate a key pair for secure access or choose an existing one. You can also configure additional settings like storage and security groups.
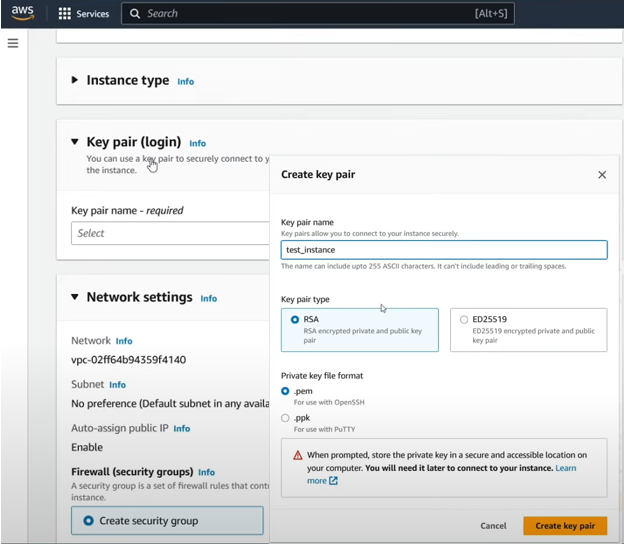
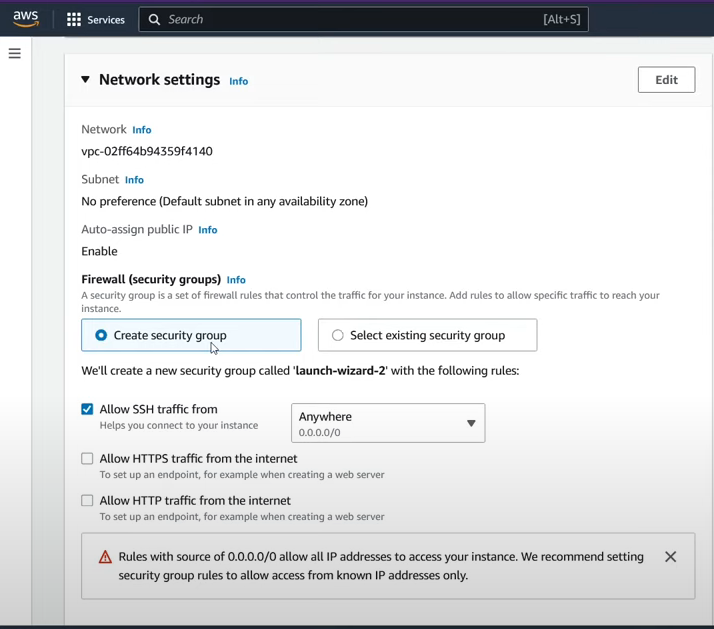
Create a Security Group: Create a Security Group and click on the checkbox to allow ssh traffic.
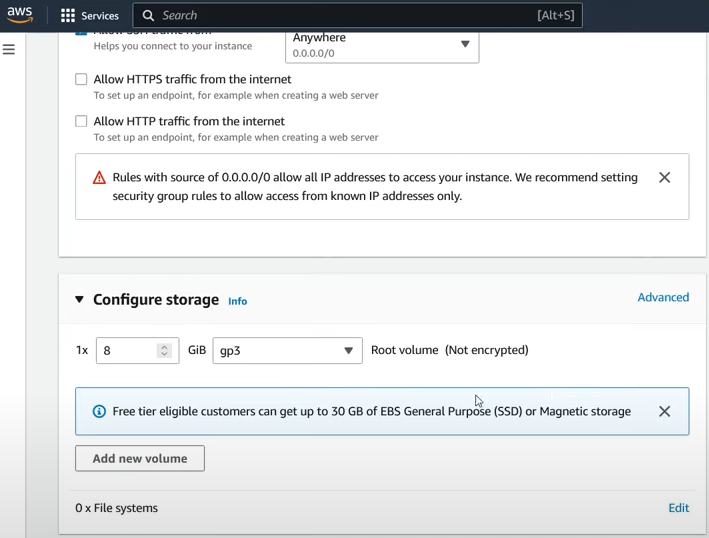
Configure Storage: Configure storage here. Free tier eligible customers can get up to 30 GB of EBS General Purpose (SSD) or Magnetic
storage. And, leave the remaining settings as default.
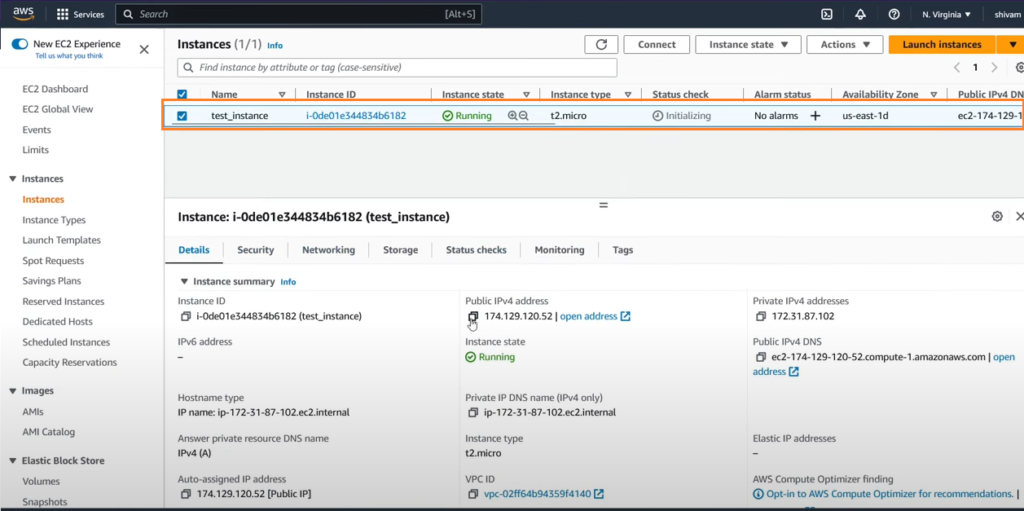
Launch the instance: Click on the Launch Instance button and it’ll initiate the instance creation process. Once launched, your virtual server will be ready for use.
Understanding Amazon EC2 Pricing
Amazon EC2 offers a variety of pricing models to cater to diverse user needs and spending preferences. Here’s a breakdown of the key options:
1. On-Demand Instances
- Pay per hour or per second (depending on the instance type) for the compute capacity you use.
- Ideal for short-term workloads, testing, and development environments.
- No upfront commitments required, offering maximum flexibility.
2. Savings Plans
- Commit to a specific usage level for a fixed term (1 or 3 years) to receive significant discounts compared to On-Demand pricing.
- Well-suited for predictable workloads with consistent resource requirements.
- Offers flexibility to adjust your commitment throughout the term based on usage changes.
3. Reserved Instances
- Purchase reserved instances for a fixed term (1 or 3 years) at a significantly lower hourly rate than On-Demand pricing.
- Provides the most significant cost savings but requires upfront commitment.
- Ideal for predictable, long-term workloads with stable resource needs.
4. Amazon EC2 Spot Instances
- Bid on unused EC2 capacity in the AWS cloud market at a discounted hourly rate.
- Spot instances are interruptible, meaning they can be stopped by AWS with a two-minute notice.
- Suitable for fault-tolerant workloads that can handle interruptions and for cost-optimization.
Choosing the Right Model
The optimal pricing model depends on your specific workload characteristics, budget considerations, and risk tolerance. Consider factors like:
- Predictability of workload: Consistent workloads favor Savings Plans or Reserved Instances, while unpredictable workloads might be better suited for On-Demand or Spot Instances.
- Budget flexibility: On-demand offers maximum flexibility but comes at a higher cost, while Reserved Instances require upfront commitment but offer significant savings.
- Risk tolerance: Spot Instances offer the lowest cost but are interruptible, requiring your application to be tolerant of interruptions.
By understanding these pricing models and carefully evaluating your needs, you can select the most cost-effective option for your EC2 instances on AWS.