Understanding vApp in vSphere: A Complete Guide
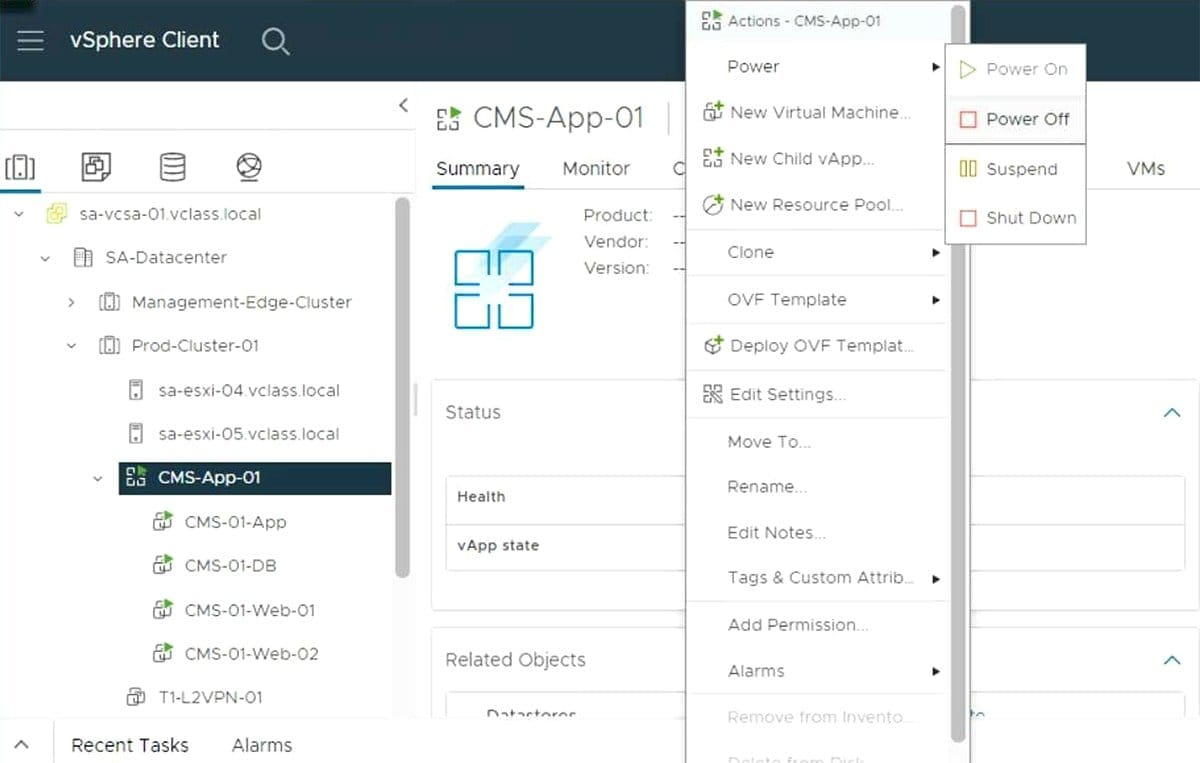
Table of Contents
Introduction
In VMware vSphere, a vApp is a logical container that allows administrators to group related virtual machines (VMs) into a single management unit. This is particularly valuable for multi-tier applications, where different components—such as web servers, application servers, and databases—must work together seamlessly.
By organizing VMs within a vApp, IT teams can manage them collectively, applying shared policies, power operations, and resource allocation. This simplifies administration and ensures consistency across interconnected workloads.
vApps also introduce advanced features like power-on sequencing, resource pooling, and custom networking configurations, which are essential for maintaining performance and reliability in enterprise environments. Whether you’re deploying a new application, cloning test environments, or preparing for disaster recovery, vApps provide the flexibility and control needed to optimize complex workloads.
Key Features of vApp
Logical Grouping of VMs
vApps are used to group VMs that share dependencies, such as multi-tier applications (web, application, and database tiers). They allow easy management of application components as a single unit.
Resource Allocation
Administrators can define resource settings (CPU, memory) at the vApp level, ensuring that the application gets adequate resources while optimizing resource usage.
Power-On Sequencing
vApps enable administrators to configure the sequence in which VMs start and stop, ensuring dependent VMs (e.g., database servers) are ready before other components (e.g., web servers) boot up.
Networking
vApps provide isolated networks for VMs within the container, simplifying network management and enhancing security. Administrators can configure advanced networking options like NAT, DHCP, and static routing.
Template and Portability
vApps can be exported as OVF (Open Virtualization Format) templates, making them portable across different environments.
Simplifies application deployment and disaster recovery.
Benefits of vApp
Simplified Application Management
When managing enterprise applications that span multiple virtual machines, vApps dramatically reduce administrative overhead. Consider a typical three-tier application: instead of managing each tier separately, you manage one vApp object. This simplification extends to cloning, moving, and backing up your entire application stack.
Consistent Deployment
vApps ensure consistency across development, testing, and production environments. By packaging your entire application stack into a single vApp, you guarantee that all environments are configured identically, reducing deployment errors and environmental inconsistencies.
Resource Control
Resource pools integrated into vApps provide granular control over CPU and memory allocation. You can set reservations, limits, and shares at the vApp level, ensuring that your critical applications receive the resources they need while preventing resource contention.
Automation and Orchestration
The startup and shutdown orchestration capabilities enable sophisticated automation scenarios. You can define delays between VM startups, ensuring services are fully initialized before dependent components begin.
vApp Architecture and Components
Resource Pools Integration
Every vApp is essentially a special type of resource pool with additional properties. This means vApps inherit all resource pool capabilities while adding application-specific features like start order and OVF compatibility.
vApp Properties
vApps support customizable properties that can be passed to guest operating systems during startup. These properties enable dynamic configuration without hardcoding values into VMs, making vApps highly portable and environment-agnostic.
Product Information
vApps can contain metadata about the application including vendor information, version numbers, and licensing details. This metadata travels with the vApp, providing documentation and version control benefits.
Step-by-Step Lab Tutorial: Deploying a 3-Tier Application with vApp in vSphere
Objective
Create a 3-tier application using a vApp in vSphere. The tiers will include:
- Web Server Tier (e.g., Apache)
- Application Server Tier (e.g., Tomcat)
- Database Tier (e.g., MySQL)
Prerequisites
- VMware vSphere environment.
- A vCenter Server.
- ISOs or templates for the required operating systems.
Steps
1. Create a vApp
Log in to the vSphere Web Client.
- Navigate to the desired Cluster or Resource Pool.
- Right-click and select New vApp.
- Name the vApp and assign resource allocation settings (CPU, memory).
- Complete the wizard.
2. Add Virtual Machines to the vApp
- Right-click the vApp and select Add VM to vApp.
- Create or import VMs for the three tiers: Web, Application, and Database.
- Assign appropriate resource allocations to each VM.
3. Configure Networking
- Right-click the vApp and select Edit Settings.
- Configure vApp Networks for internal communication.
- Use NAT or a routed network for external access.
4. Set Power-On Sequence
- Right-click the vApp and go to Edit Settings.
- Configure the power-on order:
- Start the Database VM first.
- Follow with the Application VM.
- Start the Web Server VM last.
- Set delay intervals to ensure dependencies are ready.
5. Deploy the 3-Tier Application
- Configure the database on the Database VM.
- Deploy the application logic on the Application VM.
- Set up the web server on the Web VM and connect it to the Application VM.
6. Test the Application
- Access the web application from a browser.
- Verify that all tiers are functioning correctly.
7. Export the vApp (Optional)
- Right-click the vApp and select Export OVF Template.
- Save the file for redeployment or backup.
Conclusion
VMware vApp is an indispensable tool for managing complex, multi-tier applications in vSphere environments. By containerizing related virtual machines and providing sophisticated orchestration capabilities, vApps dramatically simplify application deployment, management, and portability.
The startup order feature alone justifies vApp adoption for many organizations, eliminating manual intervention in application startup sequences and reducing errors caused by services starting before their dependencies are ready.
Combined with resource allocation controls, OVF portability, and integration with vSphere’s advanced features, vApps provide a comprehensive solution for application lifecycle management in virtualized environments.
Whether you’re deploying a simple two-tier application or a complex microservices architecture, vApps offer the structure and automation capabilities needed to manage these systems efficiently at scale. Start small with a single multi-tier application, master the concepts, and gradually expand your vApp usage across your infrastructure.









Wonderful article! We will be linking to this great article on our website.
Keep up the great writing.