VMware vSphere ESXi iSCSI Multipathing Configuration
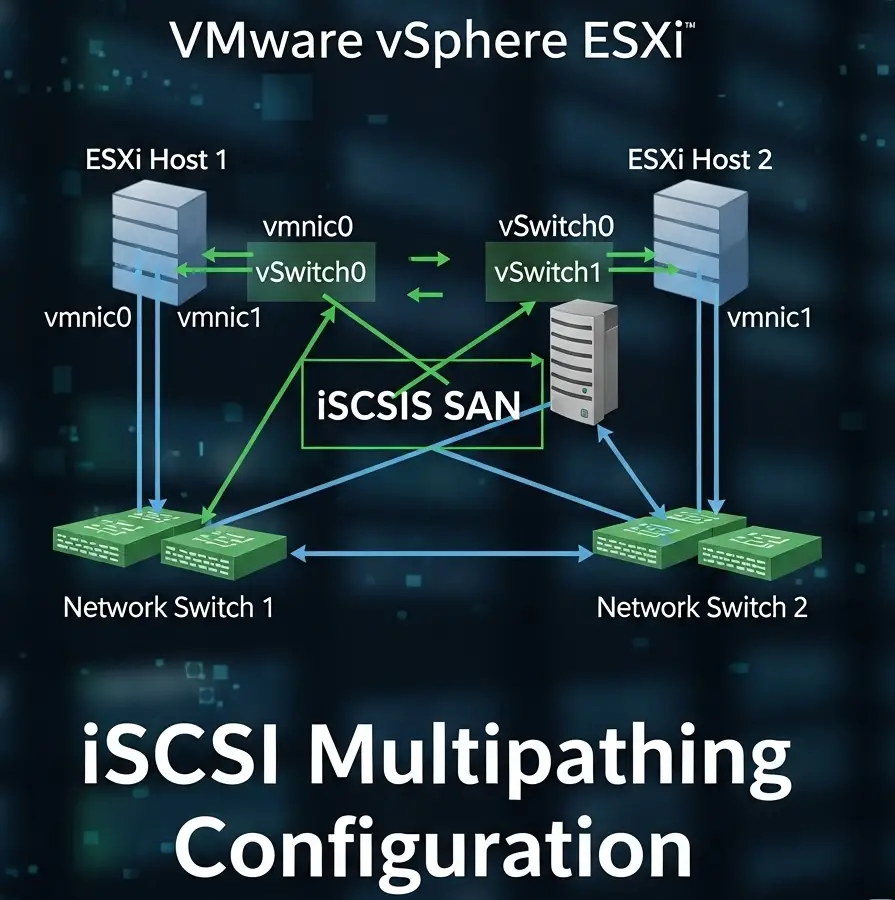
VMware vSphere ESXi iSCSI multipathing is a critical storage connectivity feature that provides redundancy, load balancing, and improved performance for virtual machine storage. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll cover the fundamentals, prerequisites, configuration steps, best practices, and troubleshooting methods for successfully implementing iSCSI multipathing in ESXi environments.
What is iSCSI Multipathing
iSCSI multipathing allows ESXi hosts to establish multiple network paths to iSCSI storage targets, ensuring high availability and optimized performance. When configured correctly, it offers:
- Storage redundancy – Eliminates single points of failure
- Load balancing – Distributes I/O across multiple network paths
- Automatic failover – Seamless switching during path or hardware failures
- Enhanced performance – Increased bandwidth through multiple paths
Benefits of ESXi iSCSI Multipathing
ESXi iSCSI multipathing offers several key benefits that enhance storage reliability and performance in virtualized environments. High availability is achieved by eliminating single points of failure, ensuring that storage connectivity remains uninterrupted even if one network path goes down. Performance gains come from leveraging multiple network interface cards (NICs) to process I/O operations simultaneously, which improves throughput and reduces latency.
The solution is also cost-effective because it operates over standard Ethernet infrastructure, eliminating the need for expensive proprietary networking hardware. Additionally, it provides excellent scalability, allowing storage connectivity to grow seamlessly alongside business needs. Finally, iSCSI multipathing offers flexibility through support for multiple Path Selection Policies (PSPs), enabling administrators to fine-tune performance and failover behavior based on specific workload requirements.
Prerequisites and Requirements
Hardware
- VMware ESXi 6.0 or later (7.0+ recommended)
- Minimum 2 network adapters for multipathing
- iSCSI-compatible storage array
- 1GbE minimum, 10GbE recommended switches
Software
- VMware vSphere Client or vCenter Server
- Licensed VMware vSphere environment
- Vendor iSCSI storage management tools
Network
- Dedicated iSCSI VLANs
- Jumbo frames support (9000 MTU)
- QoS prioritization for iSCSI traffic
- Proper IP addressing plan
Understanding iSCSI Multipathing Concepts
In VMware ESXi, understanding iSCSI multipathing concepts is essential for configuring storage performance and reliability. Path Selection Policies (PSPs) determine how I/O is distributed across available paths. The VMW_PSP_RR (Round Robin) policy, which is the default for most storage arrays, optimizes performance by rotating I/O requests evenly across all active paths.
The VMW_PSP_MRU (Most Recently Used) policy uses the last active path until it fails, switching to an alternative path only when necessary.
The VMW_PSP_FIXED policy always uses a designated preferred path and only switches during a failure, making it suitable for specific storage architectures. Equally important are path states, which define the current condition of each connection.
An Active state indicates that the path is operational and available, Dead means the path has failed and cannot be used, and Standby refers to a path that is available but not currently active. Understanding these concepts is crucial for effective multipathing configuration and troubleshooting.
Network Configuration for iSCSI Multipathing
- Dedicated VLANs:
- VLAN 100 → Primary iSCSI (192.168.100.x)
- VLAN 101 → Secondary iSCSI (192.168.101.x)
- Switch Best Practices:
- Enable jumbo frames
- Configure QoS for iSCSI traffic
- Avoid LACP for iSCSI
- Example IP Plan:
- ESXi Host: 192.168.100.10 & 192.168.101.10
- Storage Controllers: 192.168.100.20 & 192.168.101.20
Step-by-Step ESXi iSCSI Multipathing Configuration
1. Create iSCSI VMkernel Interfaces
- Networking → Add VMkernel Adapter → Assign VLAN & IP → Enable iSCSI service.
- Repeat for the second network path.
2. Enable Software iSCSI Adapter
- Storage → Adapters → Software iSCSI → Enable.
3. Bind VMkernel Interfaces
- Select iSCSI Adapter → Network Port Binding → Add both VMkernels.
4. Discover Storage Targets
- Dynamic Discovery → Add storage controller IPs → Rescan storage adapters.
5. Set Multipathing Policy
- Storage → Devices → Edit Multipathing → Select Round Robin (VMW_PSP_RR) → Set IOPS to 1.
Verification & Testing
CLI Commands
esxcli iscsi adapter list
esxcli iscsi networkportal list
esxcli storage nmp device list
esxcli storage nmp path list -d <device_id>
Failover Test
- Disconnect one path → Confirm VMs remain online → Reconnect path.
Conclusion
VMware ESXi iSCSI multipathing is essential for achieving high availability, load balancing, and optimal storage performance. By following a structured approach—planning, testing, and monitoring—you can ensure a robust, fault-tolerant storage environment.