Overview
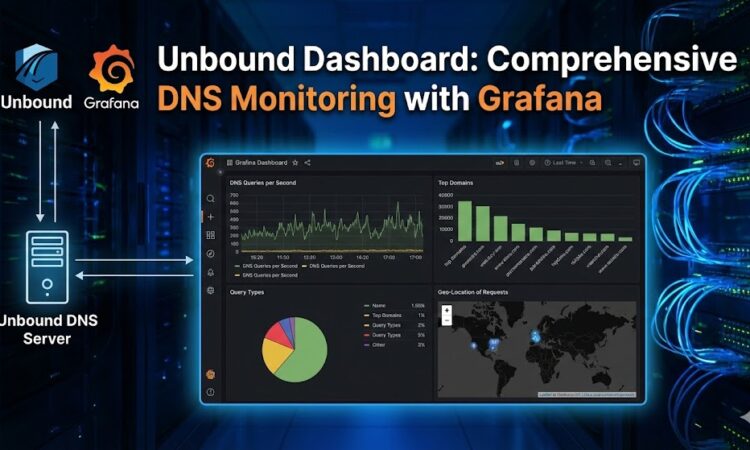
The Unbound Dashboard is a powerful monitoring solution that brings together Grafana, Prometheus, and Loki to provide comprehensive visualization and analysis of your Unbound DNS resolver. This open-source project offers real-time metrics, historical data analysis, and log aggregation in an elegant, easy-to-read interface.
What is Unbound Dashboard?
Unbound Dashboard is a complete monitoring stack specifically designed for the Unbound DNS resolver. It leverages industry-standard tools to collect, store, and visualize DNS metrics and logs, giving you deep insights into your DNS infrastructure’s performance and behavior.
Key Features
- Real-time Metrics Visualization: Monitor DNS queries, cache performance, and server health in real-time through customizable Grafana dashboards
- Historical Data Analysis: Track trends and patterns over time with Prometheus time-series database
- Log Aggregation: Collect and analyze Unbound logs using Loki for troubleshooting and security monitoring
- Efficient Custom Exporter: Built with Go for optimal performance and minimal resource footprint
- Easy Installation: Straightforward setup process with pre-configured components
- Raspberry Pi Optimized: Tested and optimized for ARM64 architecture, perfect for home labs and small deployments
Technical Architecture
The Unbound Dashboard consists of four main components working together seamlessly:
1. Grafana (v11.1.0)
The visualization layer that presents your DNS data through an intuitive web interface. The dashboard includes:
- Query statistics and trends
- Cache hit ratios
- Performance metrics
- System resource utilization
- Log analysis panels
2. Prometheus (v2.42.0)
A time-series database that scrapes and stores metrics from the Unbound exporter at regular intervals. It provides:
- Efficient data storage
- Powerful query language (PromQL)
- Reliable metric collection
- Historical data retention
3. Unbound Exporter (Go 1.21.5)
A custom-built exporter written in Go that:
- Collects extended statistics from Unbound
- Uses Unix domain sockets for faster communication
- Exports metrics in Prometheus format
- Monitors blocklist effectiveness
- Provides exporter health status
4. Loki (v3.1.0)
A log aggregation system that:
- Collects and indexes Unbound logs
- Enables powerful log queries
- Integrates seamlessly with Grafana
- Handles large datasets efficiently
Installation Requirements
The dashboard has been tested on:
- Operating System: Raspbian Bookworm ARM64 Lite
- Hardware: Raspberry Pi 4 Model B
- Unbound: Any recent version with extended statistics support
The lightweight design makes it suitable for running on modest hardware while still providing enterprise-grade monitoring capabilities.
Installation Process
The setup follows a logical progression through five main steps. Below are detailed instructions for each component.
Prerequisites
Before beginning the installation, ensure you have:
- A working Unbound DNS resolver
- Root or sudo access to your system
- Basic familiarity with Linux command line
- Adequate disk space (recommended: 10GB+ free)
- Internet connectivity for downloading packages
Step 1: Install Grafana
Grafana provides the visualization layer for your dashboard.
Download Grafana
There are two versions available: OSS (Open Source Software) and Enterprise. The OSS version is recommended as it’s lightweight and sufficient for this use case. Download the appropriate package for your architecture:
# For ARM64 (Raspberry Pi 4, etc.) wget https://dl.grafana.com/oss/release/grafana_11.1.0_arm64.deb # For AMD64/x86_64 wget https://dl.grafana.com/oss/release/grafana_11.1.0_amd64.deb
Install Dependencies
Since Grafana 10.2.3, the musl package is required:
sudo apt install musl
Install Grafana
sudo dpkg -i grafana_11.1.0_arm64.deb
Configure Grafana (Optional but Recommended)
The project provides an optimized grafana.ini configuration file that:
- Reduces memory footprint
- Disables usage statistics collection
- Stops unnecessary calls to Grafana servers
- Includes performance optimizations
To use the optimized configuration:
- Download the latest release from the GitHub repository
- Back up the default configuration:
sudo cp /etc/grafana/grafana.ini /etc/grafana/grafana.ini.backup
- Copy the optimized
grafana.inifrom the release to/etc/grafana/
Alternatively, you can use the default configuration located at /etc/grafana/grafana.ini.
Start Grafana Service
sudo systemctl daemon-reload
sudo systemctl enable grafana-server
sudo systemctl start grafana-server
Verify Installation
Check that Grafana is running:
sudo systemctl status grafana-server
Access the Grafana web interface at http://<your-server-ip>:3000/
Default credentials:
- Username:
admin - Password:
admin(you’ll be prompted to change this on first login)
Step 2: Install Prometheus
Prometheus collects and stores time-series metrics from the Unbound exporter.
Install Prometheus
sudo apt update
sudo apt install prometheus
Configure Prometheus
The project provides a trimmed-down prometheus.yml configuration optimized for Unbound monitoring.
- Back up the existing configuration:
sudo cp /etc/prometheus/prometheus.yml /etc/prometheus/prometheus.yml.backup
- Download the optimized
prometheus.ymlfrom the latest release - Copy it to the Prometheus configuration directory:
sudo cp prometheus.yml /etc/prometheus/
The optimized configuration includes:
- Unbound exporter metric collection enabled
- 5-minute scrape interval
- Default node and prometheus exporter collections removed
Remove Node Exporter (Optional)
Node exporter is installed as part of the Prometheus package but isn’t needed for the Unbound dashboard. If you’re not using it elsewhere:
sudo apt --purge autoremove prometheus-node-exporter
This removes 8 node-exporter related packages, freeing up system resources.
Restart Prometheus
sudo systemctl restart prometheus
Verify Installation
Check Prometheus status:
sudo systemctl status prometheus
Access the Prometheus web interface at http://<your-server-ip>:9090/
Step 3: Install Unbound Exporter
The Unbound exporter is a custom-built Go application that collects metrics from Unbound and exposes them for Prometheus.
Configure Unbound
First, enable the necessary features in Unbound:
- Edit the Unbound configuration file:
sudo nano /etc/unbound/unbound.conf
- Add the following option under the
server:section:
yaml
extended-statistics: yes
- Add the following options under the
remote-control:section:
yaml
control-interface: "/var/run/unbound.sock"
control-use-cert: no
These enable Unix domain socket communication, which is faster than TCP.
- Save and exit (Ctrl+X, then Y, then Enter in nano)
- Restart Unbound:
sudo systemctl restart unbound
Install the Exporter Binary
- Download the latest release from the GitHub repository
- Extract the
unbound-exporterbinary - Copy it to the system binary directory:
sudo cp unbound-exporter /usr/local/bin/
- Set proper ownership and permissions:
sudo chown root:root /usr/local/bin/unbound-exporter
sudo chmod +x /usr/local/bin/unbound-exporter
Create Systemd Service
To run the exporter automatically at startup:
- Download
prometheus-unbound-exporter.servicefrom the release - Copy it to the systemd directory:
sudo cp prometheus-unbound-exporter.service /etc/systemd/system/
- Ensure proper ownership:
sudo chown root:root /etc/systemd/system/prometheus-unbound-exporter.service
The service file includes parameters for:
- Blocklist file path
- Unbound Unix domain socket URI
Modify these if you use different paths or names.
Enable and Start the Service
sudo systemctl daemon-reload
sudo systemctl enable prometheus-unbound-exporter
sudo systemctl start prometheus-unbound-exporter
Verify Installation
Check the service status:
sudo systemctl status prometheus-unbound-exporter
The exporter runs on port 9167 by default. You can test it by accessing:
curl http://localhost:9167/metrics
This should display Prometheus-formatted metrics.
Exporter Usage
To see available command-line options:
unbound-exporter -h
Step 4: Install Loki and Promtail
Loki aggregates and indexes logs, while Promtail scrapes and sends logs to Loki.
Download Loki and Promtail
# For ARM64
curl -O -L "https://github.com/grafana/loki/releases/download/v3.1.0/loki_3.1.0_arm64.deb"
curl -O -L "https://github.com/grafana/loki/releases/download/v3.1.0/promtail_3.1.0_arm64.deb"
# For AMD64
curl -O -L "https://github.com/grafana/loki/releases/download/v3.1.0/loki_3.1.0_amd64.deb"
curl -O -L "https://github.com/grafana/loki/releases/download/v3.1.0/promtail_3.1.0_amd64.deb"
Install Loki and Promtail
sudo dpkg -i loki_3.1.0_arm64.deb
sudo dpkg -i promtail_3.1.0_arm64.deb
Enable Unbound Logging
- Edit the Unbound configuration:
sudo nano /etc/unbound/unbound.conf
- Add or modify these options under the
server:section:
yaml
log-replies: yes
log-tag-queryreply: yes
log-local-actions: yes
logfile: /var/log/unbound/unbound.log
Important: Ensure verbosity: is set to 0.
- Save and exit
Create Log Directory
sudo mkdir /var/log/unbound
sudo chown unbound:unbound /var/log/unbound
Configure Log Rotation
To prevent log files from consuming too much disk space:
- Download the
unboundlogrotate configuration from the release (under thelogrotatedirectory) - Copy it to the logrotate directory:
sudo cp unbound /etc/logrotate.d/
- Ensure proper ownership:
sudo chown root:root /etc/logrotate.d/unbound
Configure Loki
- Download the optimized
config.ymlfrom the release (under thelokidirectory) - Back up the existing configuration:
sudo cp /etc/loki/config.yml /etc/loki/config.yml.backup
- Replace it with the optimized version:
sudo cp config.yml /etc/loki/
- Ensure proper ownership:
sudo chown root:root /etc/loki/config.yml
The optimized Loki configuration is tuned to:
- Process large datasets efficiently
- Handle multiple concurrent queries
- Calculate metrics from Unbound logs
- Prevent timeouts with large data volumes
Configure Promtail
- Download the optimized
config.ymlfrom the release (under thepromtaildirectory) - Back up the existing configuration:
sudo cp /etc/promtail/config.yml /etc/promtail/config.yml.backup
- Replace it with the optimized version:
sudo cp config.yml /etc/promtail/
- Ensure proper ownership:
sudo chown root:root /etc/promtail/config.yml
The Promtail configuration enables scraping of Unbound logs.
Restart Services
sudo systemctl restart unbound
sudo systemctl restart loki
sudo systemctl restart promtail
Verify Installation
Check service statuses:
sudo systemctl status loki
sudo systemctl status promtail
Verify that Unbound is logging:
sudo tail -f /var/log/unbound/unbound.log
Step 5: Import the Dashboard
Now that all components are installed, it’s time to set up the dashboard in Grafana.
Configure Data Sources
- Open Grafana in your web browser:
http://<your-server-ip>:3000/ - Log in with your credentials
- Navigate to Configuration → Data Sources (or use the gear icon in the left sidebar)
Add Prometheus Data Source
- Click Add data source
- Select Prometheus
- Configure the following options:
- Name:
Prometheus - Default: Toggle to On
- URL:
http://localhost:9090 - Scrape interval:
5m
- Scroll down and click Save & test
You should see a green message confirming the connection.
Add Loki Data Source
- Click Add data source again
- Select Loki
- Configure the following options:
- Name:
Loki - URL:
http://localhost:3100 - Maximum lines:
100000
- Scroll down and click Save & test
You should see a confirmation message.
Import the Dashboard
- Download
unbound-dashboard.jsonfrom the latest release - In Grafana, navigate to Dashboards → Import (or click the “+” icon in the left sidebar and select “Import”)
- Click Upload JSON file
- Select the
unbound-dashboard.jsonfile you downloaded - Configure the import options:
- Folder: Select
Dashboardsor create a new folder - Prometheus: Select the Prometheus data source you created
- Loki: Select the Loki data source you created
- Click Import
The dashboard should now load, displaying your Unbound DNS metrics and logs!
Set Dashboard as Home Page (Optional)
To make the Unbound dashboard your landing page:
- Click on your profile icon in the top-right corner
- Select Profile
- Under Preferences, find Home Dashboard
- Select General/Unbound from the dropdown
- Optionally, change the interface theme (Dark/Light)
- Click Save
Now the Unbound dashboard will load automatically when you access Grafana.
Post-Installation Configuration
Verify Data Collection
After installation, verify that data is being collected:
- Wait 5–10 minutes for initial data collection
- Open the Unbound dashboard in Grafana
- Check that panels are populating with data
- Review the time range selector (top-right) to view different time periods
Troubleshooting
Check Unbound Exporter:
sudo systemctl status prometheus-unbound-exporter
curl http://localhost:9167/metrics
Check Prometheus:
udo systemctl status prometheus
# Visit http://<your-server-ip>:9090/targets to see scrape targets
Check Loki and Promtail:
sudo systemctl status loki
sudo systemctl status promtail
sudo tail -f /var/log/unbound/unbound.log
Check Unbound:
sudo systemctl status unbound
sudo unbound-control stats
Customizing the Dashboard
Once installed, you can customize the dashboard:
- Adjust time ranges for different panels
- Modify query intervals
- Add or remove panels
- Create custom alerts
- Change visualization types
- Adjust thresholds and colors
Advanced Configuration Tips
Optimize Prometheus Data Retention
By default, Prometheus retains data for 15 days. To adjust this:
- Edit the Prometheus defaults:
sudo nano /etc/default/prometheus
- Add or modify the
ARGSline:
ARGS="--storage.tsdb.retention.time=30d"
- Restart Prometheus:
sudo systemctl restart prometheus
Enable Prometheus Admin API
The Admin API allows you to delete specific metrics or perform maintenance:
- Edit the Prometheus defaults:
sudo nano /etc/default/prometheus
- Add the following at the top:
ARGS="--web.enable-admin-api --log.level=warn"
- Restart Prometheus:
sudo systemctl restart prometheus
- To delete metrics from a specific job:
# Delete all metrics from a job (e.g., "node")
curl -X POST -g 'http://localhost:9090/api/v1/admin/tsdb/delete_series?match[]={job="node"}'
# Clean up tombstones
curl -X POST -g 'http://localhost:9090/api/v1/admin/tsdb/clean_tombstones'
# Restart Prometheus
sudo systemctl restart prometheus
Reduce System Log Verbosity
To minimize disk I/O and log file sizes:
For Prometheus: Already configured in the ARGS with --log.level=warn
For Loki: Edit /etc/loki/config.yml and set log level to warn or error
For Grafana: Edit /etc/grafana/grafana.ini and adjust the logging section:
ini
[log]
mode = console file
level = warn
Configure Grafana Email Alerts
To receive email notifications for critical metrics:
- Edit Grafana configuration:
sudo nano /etc/grafana/grafana.ini
- Configure SMTP settings:
ini
[smtp]
enabled = true
host = smtp.gmail.com:587
user = your-email@gmail.com
password = your-app-password
from_address = your-email@gmail.com
from_name = Grafana Unbound
- Restart Grafana:
sudo systemctl restart grafana-server
- In the dashboard, configure alert rules for panels you want to monitor
Performance Tuning for Low-Resource Systems
If running on a Raspberry Pi or similar device:
Reduce Scrape Frequency: Edit /etc/prometheus/prometheus.yml and increase scrape_interval:
yaml
global:
scrape_interval: 10m # Instead of 5m
Limit Log Collection: Edit /etc/promtail/config.yml and add filters to reduce log volume
Adjust Loki Retention: Edit /etc/loki/config.yml to reduce retention period:
yaml
table_manager:
retention_deletes_enabled: true
retention_period: 168h # 7 days instead of default
Backup Your Configuration
Regular backups are essential:
# Create a backup directory
sudo mkdir -p /backup/unbound-dashboard
# Backup Grafana database
sudo cp /var/lib/grafana/grafana.db /backup/unbound-dashboard/# Backup all configurations
sudo cp /etc/grafana/grafana.ini /backup/unbound-dashboard/
sudo cp /etc/prometheus/prometheus.yml /backup/unbound-dashboard/
sudo cp /etc/loki/config.yml /backup/unbound-dashboard/
sudo cp /etc/promtail/config.yml /backup/unbound-dashboard/
sudo cp /etc/unbound/unbound.conf /backup/unbound-dashboard/# Create a tar archive
cd /backup
sudo tar -czf unbound-dashboard-backup-$(date +%Y%m%d).tar.gz unbound-dashboard/
Consider setting up a cron job to automate backups.
What You Can Monitor
The dashboard provides visibility into numerous aspects of your DNS resolver:
Performance Metrics
- Queries per second
- Response times
- Cache hit ratios
- Thread utilization
- Memory usage
Query Analysis
- Query types (A, AAAA, PTR, etc.)
- Top queried domains
- Blocked queries
- DNSSEC validation statistics
- Upstream server performance
Security Insights
- Blocked domain statistics
- Query sources
- Unusual query patterns
- Failed lookups
- DNSSEC failures
System Health
- Exporter status
- Server uptime
- Resource utilization
- Error rates
- Warning indicators
Optimization Features
The project includes several optimizations:
Grafana Configuration
- Reduced memory footprint
- Disabled usage collection
- Eliminated external calls to Grafana servers
- Streamlined settings for dedicated DNS monitoring
Prometheus Configuration
- Optimized scraping intervals (5 minutes)
- Focused metric collection
- Removed unnecessary exporters
- Efficient storage configuration
Loki Configuration
- Tuned for large log datasets
- Optimized query performance
- Configured for DNS-specific log patterns
- Enhanced metric calculation
Conclusion
The Unbound Dashboard represents a comprehensive, efficient, and user-friendly solution for monitoring DNS infrastructure. Whether you’re running Unbound on a Raspberry Pi in your home lab or managing DNS for a small organization, this dashboard provides the insights you need to ensure optimal performance and security.
With its combination of real-time metrics, historical analysis, and log aggregation, the Unbound Dashboard transforms raw DNS data into actionable insights, all presented through Grafana’s elegant interface.