How to deploy a Firewall Appliance with High Availability in VMware Cloud Director
When customers deploy their services in a Cloud Datacenter powered by VMware Cloud Director , they often want to use their own virtual firewall appliance, rather than using the Edge and Distributed firewall built into the NSX infrastructure. Many administrators prefer to use their well-known firewalls such as CheckPoint, Fortinet or pfSense for hassle-free configuration management. Using standalone virtual firewall appliances is generally fine, but in HA (High Availability) deployments there are challenges that can be addressed with features implemented in new versions of VMware Cloud Director.
This article explains
how to deploy high-availability Firewall Appliances in
VMware Cloud Director version 10.5.
As mentioned, deploying a Virtual Firewall Appliance on its own is easy. A common practice is to configure the external interface to a “Routed Network” and the internal interface to an “Isolated Network.” In this case, traffic is routed through the virtual firewall and can be filtered. A more complex setup with an HA configuration requires a feature that has only been available since Cloud Director 10.3.2: Network Segment Profiles.
For redundancy, most systems use the Virtual Router Redundancy Protocol (VRRP), which is described in RFC 3768 and RFC 5798. VRRP allows routers and firewalls to share a virtual IP address (VIP) that can be switched between two appliances in an active-passive mode. The virtual IP address uses a MAC Address in the following format: 00-00-5E-00-01-{VRID}. With the default configuration in NSX-T and VMware Cloud Director, it is not possible to have a second MAC address on an interface. To allow multiple MAC addresses per port, the port must be configured with MAC Learning enabled. While this feature has been enabled in NSX-T for some time through Segment Profiles, it is only available for use in Cloud Director version 10.3.2.
Infrastructure example
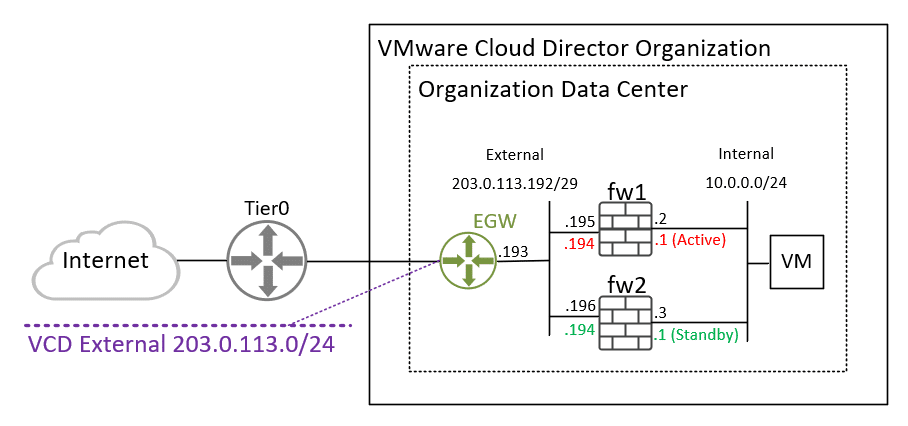
- The External Network is a Public Segment that uses IP Spaces (a feature of Cloud Director 10.4). You can also use a regular Routed Segment with private addresses.
- Virtual firewalls (fw1 and fw2) are of the VyOS type (Download: VyOS version 1.2.9)
Step 1 – Create “MAC Discovery Profile” in NSX-T
- In NSX-T, go to Networking > Segments > Profiles.
- Click ADD SEGMENT PROFILE and select the MAC Discovery option.
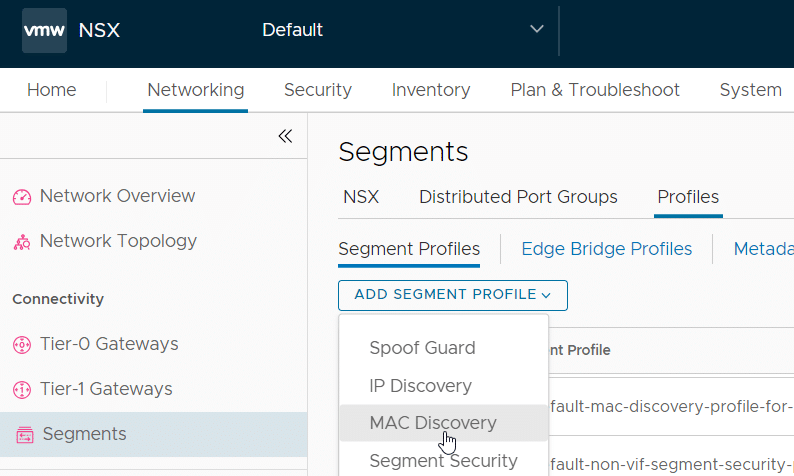
Create a new MAC Discovery Profile named “mac-learning” and enable MAC Learning.
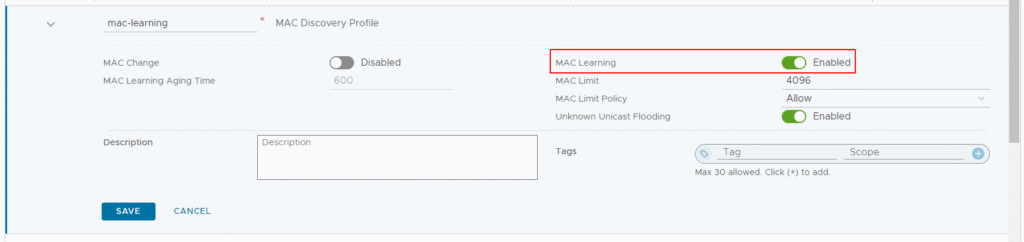
Then click SAVE.
Step 2 – Add Segment Profile in Cloud Director
Log in to VMware Cloud Director as System Administrator.
Navigate to Resources > Infrastructure Resources > NSX-T > Segment Profile Templates.
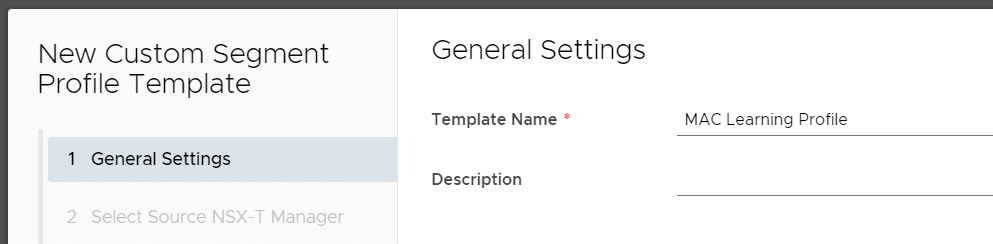
- Click NEW.
- Enter a name for the template.
- Select the NSX-T Manager instance.
- Set the MAC Discovery Profile to the Segment Profile created in NSX-T (mac-learning).
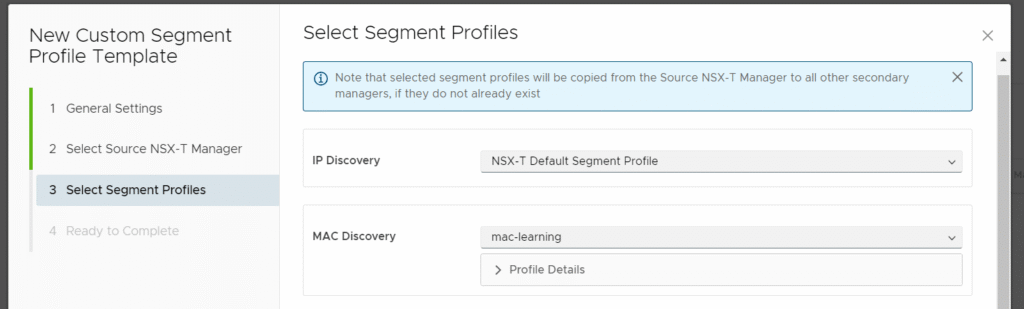
Step 3 – Enable Segment Profiles for Tenants
By default, tenants cannot view or configure Segment Profiles for their networks. To do this, the Organization needs a Rights Bundle and the user must have a Role that allows them to work with Segment Profile Templates. To choose which Organizations can modify Segment Profiles, I create a new Rights Bundle and publish it to specific Organizations. If you want this feature to be enabled for all Organizations, you can just edit the default Rights Bundle.
Steps
Log in to VMware Cloud Director as System Administrator.Go to Administration > Tenant Access Control > Rights Bundle.Click ADD.Give the Rights Bundle a name and description and add the following rights:
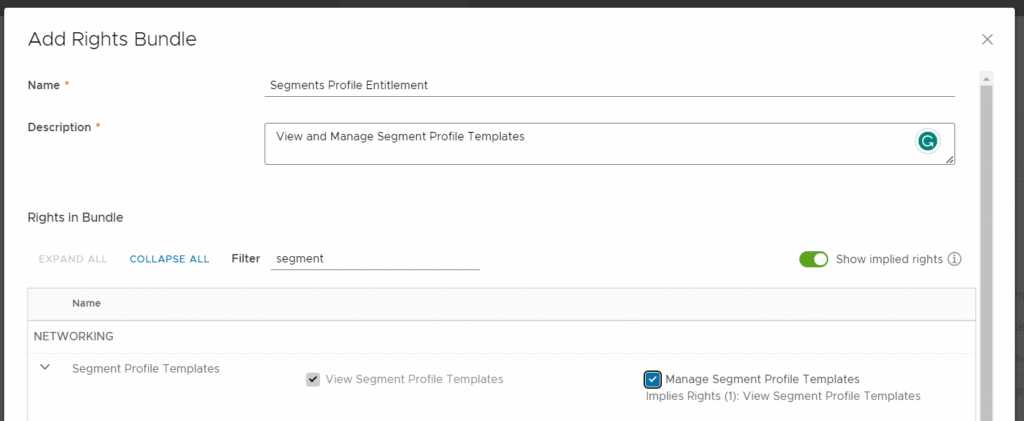
- Click SAVE.
- Select the new Rights Bundle.
- Click Publish.
- Select the organizations to which this Rights Bundle should be assigned.
With this Rights Bundle, the Organization Administrator can create a custom role with Segment Profile rights. In my opinion, it would be better to edit the default Organization Administrator role and add the Segment Profiles right to it. This does not mean that every Organization Administrator can use this feature; they still need the Rights Bundle.
To do this:
- Go to Administration > Tenant Access Control > Global Rights.
- Select the Organization Administrator role and click EDIT.
- Keep all existing rights and add the following rights:
- View Segment Profile Templates
- Manage Segment Profile Templates Implies Right
- Click SAVE.
From the Service Provider side, you’re done. Tenants who have this Rights Bundle will now see a new configuration option for Segment Profiles when creating or editing networks.
Tenant Configuration
To test this feature, I will create the following virtual infrastructure:
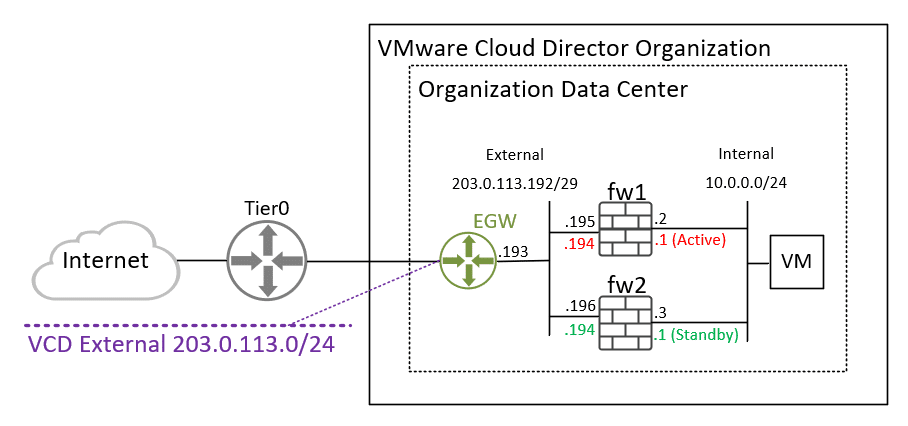
Create 2 networks with the following configurations:
- Name: External | Type: Routed | Gateway CIDR: 203.0.113.193/29
- Name: Internal | Type: Isolated | Gateway CIDR: 10.0.0.1/24
Note that the Isolated network is not connected to the Edge Gateway and therefore, the configured Gateway CIDR is still free and usable. The purpose of setting the IP address here is to automatically configure a default Gateway and network information on the VMs that are connected to this network via Guest Customization.
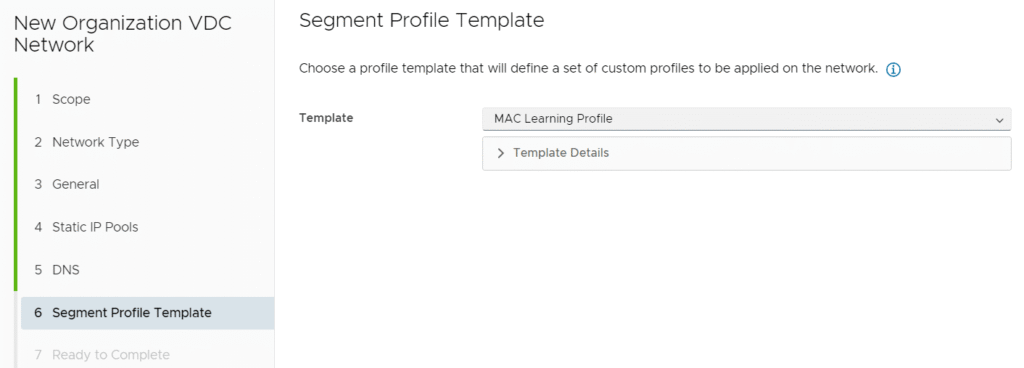
When creating, set the Segment Profile Template to MAC Learning Profile for both networks.
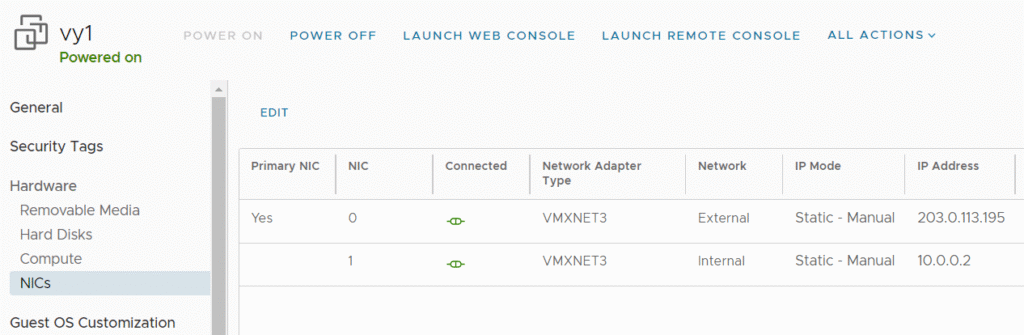
Deploy your virtual firewalls and configure virtual network cards (virtual NICs) according to the diagram.
vy1
External: 203.0.113.195
Internal: 10.0.0.2
vy2
External: 203.0.113.196
Internal: 10.0.0.3
Default Route for both: 203.0.113.193
To configure VyOS, log in with the default username and password vyos/vyos and enter configuration mode with the conf command.
vy1
set system host-name vy1
set interfaces ethernet eth0 address 203.0.113.195/29
set interfaces ethernet eth0 description OUTSIDE
set interfaces ethernet eth1 address 10.0.0.2/24
set interfaces ethernet eth1 description INSIDE
set protocols static route 0.0.0.0/0 next-hop 203.0.113.193
set service ssh port 22
set nat source rule 100 outbound-interface eth0
set nat source rule 100 source address 10.0.0.0/24
set nat source rule 100 translation address masquerade
vy2
set system host-name vy2
set interfaces ethernet eth0 address 203.0.113.196/29
set interfaces ethernet eth0 description OUTSIDE
set interfaces ethernet eth1 address 10.0.0.3/24
set interfaces ethernet eth1 description INSIDE
set protocols static route 0.0.0.0/0 next-hop 203.0.113.193
set service ssh port 22
set nat source rule 100 outbound-interface eth0
set nat source rule 100 source address 10.0.0.0/24
set nat source rule 100 translation address masquerade
Warning: Configuring VyOS this way allows SSH access from both internal and external interfaces, which is very insecure. If you plan to use it in a production environment, refer to the VyOS Quick Start to set up basic firewall rules.
To enable the configuration and save it permanently, run the following commands:
# commit
#save
The next step is to configure VRRP. Run the following commands on both systems. These commands will create a VRRP group for each interface with a shared Virtual IP. Both groups will be placed in a Sync Group so that the MASTER and BACKUP roles are always on the same system.
set high-availability vrrp group eth0 vrid 10
set high-availability vrrp group eth0 rfc3768-compatibility
set high-availability vrrp group eth0 interface eth0
set high-availability vrrp group eth0 virtual-address 203.0.113.194/29
set high-availability vrrp group eth1 vrid 11
set high-availability vrrp group eth1 rfc3768-compatibility
set high-availability vrrp group eth1 interface eth1
set high-availability vrrp group eth1 virtual-address 10.0.0.1/24
set high-availability vrrp sync-group MAIN member eth0
set high-availability vrrp sync-group MAIN member eth1
Don’t forget to run the commit and save commands to activate the configuration. You can view the VRRP status with the show vrrp command:
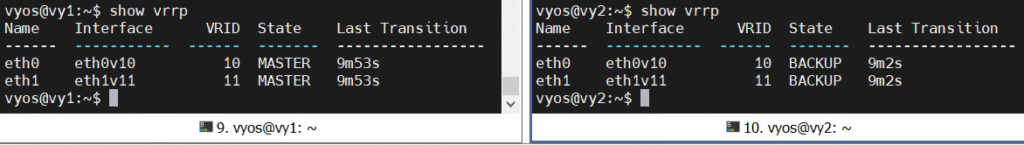
The VMs on the 10.0.0.0/24 network with the default gateway set to 10.0.0.1 should be able to access the internet. To test HA, power down the MASTER router, and it should failover within a few seconds (the default VRRP settings failover after 3 failed heartbeats sent every second).
To access internal services, configure a Destination NAT on the VRRP virtual interface:
set nat destination rule 10 destination port '80'
set nat destination rule 10 inbound-interface 'eth0v10'
set nat destination rule 10 protocol 'tcp'
set nat destination rule 10 translation address '10.0.0.11'
Note: If the external network is in a private, non-advertised range, you must also configure DNAT on the Edge Gateway in Cloud Director.