Modernizing Edge Infrastructure: Single-Node vSphere Supervisor in VMware Cloud Foundation 9
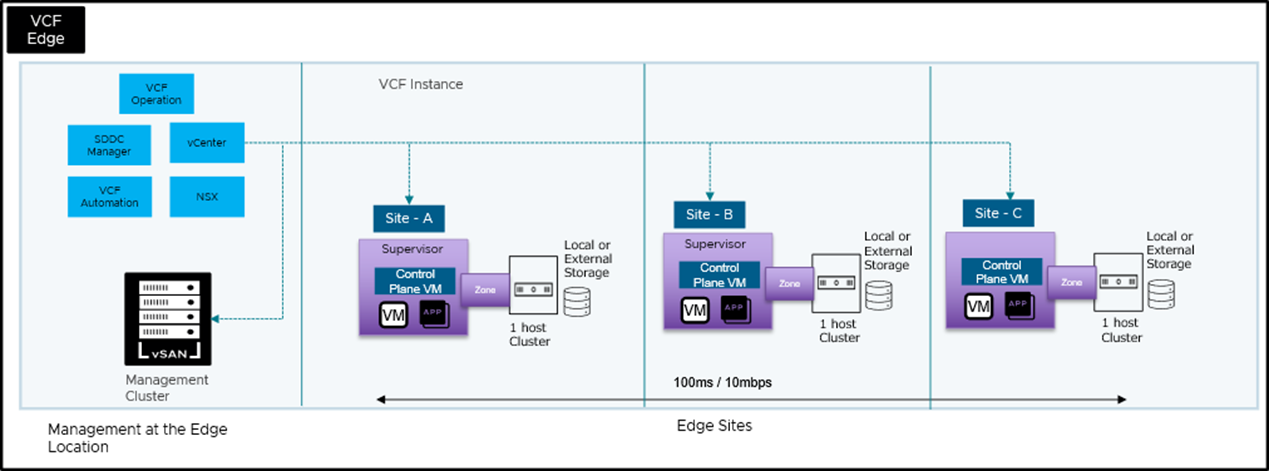
Table of Contents
Introduction
The digital transformation landscape continues to evolve rapidly, with edge computing becoming a critical component for organizations seeking to process data closer to its source. Today, digital transformation is at the front and center of every business and “data” is one of the foundational elements of this digital transformation. With the release of VMware Cloud Foundation 9.0, organizations now have powerful new capabilities to modernize their edge infrastructure while maintaining the flexibility and control of a unified private cloud platform.
This comprehensive guide explores how single-node vSphere Supervisor deployments within VMware Cloud Foundation 9 can transform edge computing strategies, enabling organizations to deploy Kubernetes workloads efficiently at remote locations with minimal infrastructure overhead.
Understanding the Edge Computing Challenge
Edge computing presents unique challenges that traditional centralized infrastructure cannot adequately address. Organizations need to bring computing power closer to data sources to reduce latency, improve response times, and enable real-time decision making. However, deploying and managing infrastructure at numerous edge locations introduces complexity around resource constraints, management overhead, and operational consistency.
The remote office/branch office (ROBO) topology has become increasingly important as businesses across all industries are running more and more applications at edge locations. While these applications were traditionally run in virtual machines, the emergence of Kubernetes and microservices architectures has created demand for cloud-native compute stacks at the edge.
VMware Cloud Foundation 9.0: A Game-Changer for Edge Modernization
VMware Cloud Foundation 9.0 represents a significant advancement in private cloud infrastructure, redefining what a modern private cloud can be — combining the speed and flexibility of the cloud experience with the performance, governance, and cost control enterprises need on-prem. This release introduces enhanced capabilities that are particularly valuable for edge deployments.
Key Features of VMware Cloud Foundation 9.0
The latest version brings several improvements that directly benefit edge computing scenarios:
Enhanced Performance and Efficiency: General availability of VMware vSphere Foundation 9.0 brings powerful new capabilities to improve efficiency, scale performance, and strengthen security. These improvements are crucial for edge environments where resource optimization is paramount.
Unified Cloud Operating Model: With the general availability of VMware Cloud Foundation (VCF) 9.0, IT teams are empowered to combine the speed and flexibility of the cloud experience with the performance, governance, and cost control enterprises need. This unified approach simplifies management across distributed edge locations.
Modern Application Support: Organizations must support legacy applications while adopting modern, containerized workloads, leading to fragmented systems and inefficiencies. VCF 9.0 addresses this challenge by providing a platform that seamlessly supports both traditional and modern workloads.
Single-Node vSphere Supervisor: Optimizing for Edge
The single-node vSphere Supervisor deployment model is particularly well-suited for edge environments where physical space, power, and cooling are limited. This approach allows organizations to deploy Kubernetes capabilities with minimal infrastructure requirements while maintaining enterprise-grade functionality.
Benefits of Single-Node Deployment
Resource Efficiency: Single node Supervisor Control Plane VM for vSphere with Tanzu now possible in vSphere 7.0 Update 3 enables organizations to run Kubernetes workloads on a single host, significantly reducing hardware requirements at edge locations.
Simplified Management: Single-node deployments reduce the complexity of managing multiple hosts while still providing the full capabilities of vSphere Supervisor, including container orchestration and lifecycle management.
Cost Optimization: By reducing the infrastructure footprint, organizations can deploy edge capabilities more cost-effectively across numerous locations.
Tanzu Kubernetes Grid for Edge Computing
VMware Tanzu Kubernetes Grid (TKG) plays a crucial role in edge modernization strategies. Tanzu Kubernetes Grid 2.1 introduced a new feature of single node clusters and also using a minimal operating system to reduce the footprint even further. This innovation is particularly valuable for edge deployments where resource constraints are a primary concern.
Single-Node Cluster Architecture
A single node cluster will create one Tanzu Kubernetes control plane node and remove the taint that allows applications to be deployed as if it were a worker node. This approach maximizes resource utilization while maintaining Kubernetes functionality.
The architecture provides several advantages:
- Reduced Footprint: Minimal resource requirements make deployment feasible in constrained environments
- Simplified Operations: Single-node management reduces operational complexity
- Edge-Optimized Runtime: Purpose-built for edge computing scenarios
Hub-and-Spoke Architecture
This demonstration shows how to use VMware Tanzu Kubernetes Grid in a hub-and-spoke architecture to create Kubernetes clusters at multiple edge locations. This model enables centralized management while providing local processing capabilities.
Implementation Strategy
Planning and Prerequisites
Before implementing single-node vSphere Supervisor at the edge, organizations should consider:
- Infrastructure Requirements: Assess the minimum hardware specifications needed for single-node deployments
- Network Connectivity: Ensure reliable connectivity between edge locations and the central management plane
- Security Considerations: Implement appropriate security measures for distributed deployments
- Monitoring and Observability: Plan for comprehensive monitoring across edge locations
Deployment Best Practices
Start Small, Scale Gradually: Begin with pilot deployments at select edge locations to validate the approach before broader rollout.
Standardize Configurations: Create standardized deployment templates to ensure consistency across locations.
Automate Where Possible: Leverage automation tools to reduce manual intervention and ensure consistent deployments.
Plan for Disconnected Operations: Design solutions that can operate during network outages or intermittent connectivity.
Operational Considerations
Managing single-node vSphere Supervisor deployments requires careful consideration of ongoing operations:
Updates and Patching: Check out our latest Hands-on Lab and experience Lifecycle Manager, Resource Management, Live Patch, Memory tiering and more in a live VCF 9 environment. These tools help maintain edge deployments efficiently.
Monitoring and Alerting: Implement comprehensive monitoring to quickly identify and resolve issues at remote locations.
Backup and Recovery: Establish robust backup strategies that account for the distributed nature of edge deployments.
Security at the Edge
Edge deployments introduce unique security challenges that must be addressed:
- Zero Trust Architecture: Implement zero trust principles for edge-to-core communication
- Local Security Policies: Deploy security policies that can operate independently of central connectivity
- Regular Security Updates: Maintain up-to-date security patches across all edge locations
Real-World Use Cases
Retail and Point-of-Sale Systems
Retail organizations can leverage single-node vSphere Supervisor deployments to modernize point-of-sale systems, enabling real-time inventory management and customer analytics at individual stores.
Manufacturing and Industrial IoT
Manufacturing facilities can deploy edge computing capabilities to process sensor data locally, enabling predictive maintenance and quality control applications with minimal latency.
Healthcare and Remote Monitoring
Healthcare providers can use edge deployments to process patient monitoring data locally, ensuring privacy compliance while enabling real-time alerts and decision support.
Migration Strategies
From Legacy to Modern
Organizations moving from traditional edge deployments to modern containerized workloads should consider a phased approach:
- Assessment Phase: Evaluate current edge infrastructure and identify modernization opportunities
- Pilot Implementation: Deploy single-node vSphere Supervisor at select locations
- Application Migration: Gradually migrate applications to containerized deployments
- Full Rollout: Scale the solution across all edge locations
Hybrid Approaches
Tanzu Standard provides multi-cloud support, enabling Kubernetes deployment across on-premises, public cloud, and edge environments. This flexibility allows organizations to adopt hybrid strategies that best fit their specific requirements.
Performance Optimization
Resource Management
Single-node deployments require careful resource management to ensure optimal performance:
- CPU and Memory Allocation: Balance between control plane and workload requirements
- Storage Optimization: Implement efficient storage strategies for both system and application data
- Network Configuration: Optimize network settings for both local and remote connectivity
Monitoring and Tuning
Continuous monitoring and performance tuning are essential for edge deployments:
- Real-time Metrics: Implement comprehensive monitoring of resource utilization
- Automated Scaling: Configure autoscaling policies where appropriate
- Performance Baselines: Establish performance baselines for comparison and troubleshooting
Future Considerations
Emerging Technologies
As edge computing continues to evolve, organizations should consider emerging technologies:
- 5G Integration: Leverage 5G connectivity for improved edge-to-cloud communication
- AI/ML at the Edge: Deploy machine learning workloads closer to data sources
- Edge-Native Applications: Develop applications specifically designed for edge deployment
Scalability Planning
Plan for growth and changing requirements:
- Capacity Planning: Anticipate future resource needs at edge locations
- Technology Evolution: Stay current with VMware roadmap and emerging capabilities
- Business Alignment: Ensure edge strategy aligns with broader business objectives
Conclusion
The combination of VMware Cloud Foundation 9.0 and single-node vSphere Supervisor deployments represents a powerful solution for edge modernization. By leveraging these technologies, organizations can deploy Kubernetes capabilities at edge locations with minimal infrastructure overhead while maintaining enterprise-grade functionality and security.
Success in edge modernization requires careful planning, thoughtful implementation, and ongoing operational excellence. Organizations that embrace this approach will be well-positioned to capitalize on the benefits of edge computing while maintaining the flexibility to adapt to future requirements.
The journey toward edge modernization is complex, but with the right tools and strategies, organizations can achieve their goals of bringing compute power closer to data sources while maintaining operational efficiency and security. VMware Cloud Foundation 9.0 and single-node vSphere Supervisor provide the foundation for this transformation, enabling organizations to build resilient, scalable edge computing solutions that support their digital transformation initiatives.