Virtualization technologies are gaining popularity in tandem with the evolving technology industry, providing the ability to optimize infrastructure, cut costs, and achieve enhanced control over IT environments.
If you need to move a virtual machine or its storage without disrupting its services, you can employ live migration by creating several virtual machines on a single ESXi host. This enables seamless switching between virtual machines while ensuring continuous service operation.
VMware vMotion and Storage vMotion stand out as leading virtualization technologies for live migration. They empower the seamless relocation of virtual machines (VMs) and their storage across physical servers, storage devices, and different data centers, minimizing downtime. Despite sharing some similarities, these technologies exhibit notable distinctions.
VMware vMotion and Storage vMotion stand out as leading virtualization technologies for live migration.
The crucial distinction lies in how these technologies handle the migration of VMs and their storage. To determine the appropriate choice, it’s essential to comprehend their operational nuances. This blog offers insights into VMware vMotion and Storage vMotion, highlighting their key variances. Additionally, we’ll delve into the advantages and challenges inherent in each technology.
With this information, you can make informed decisions on utilizing these technologies to maximize your virtualization investment.
Overview of VMware vMotions and How It Operates
VMware vMotion allows for the seamless transfer of virtual machines between physical servers, ensuring uninterrupted operation. This facilitates enhanced performance and availability of your VMs through efficient server consolidation, maintenance, and load balancing. Beyond minimizing downtime, this technology enables your team to optimize the data center by consolidating resources and maximizing hardware utilization.
Moreover, vMotion enhances the scalability and availability of your IT infrastructure, enabling the prevention of widespread disruptions or data loss by proactively migrating virtual machines from aging or consistently underperforming devices. This not only boosts adaptability but also enhances hardware optimization.
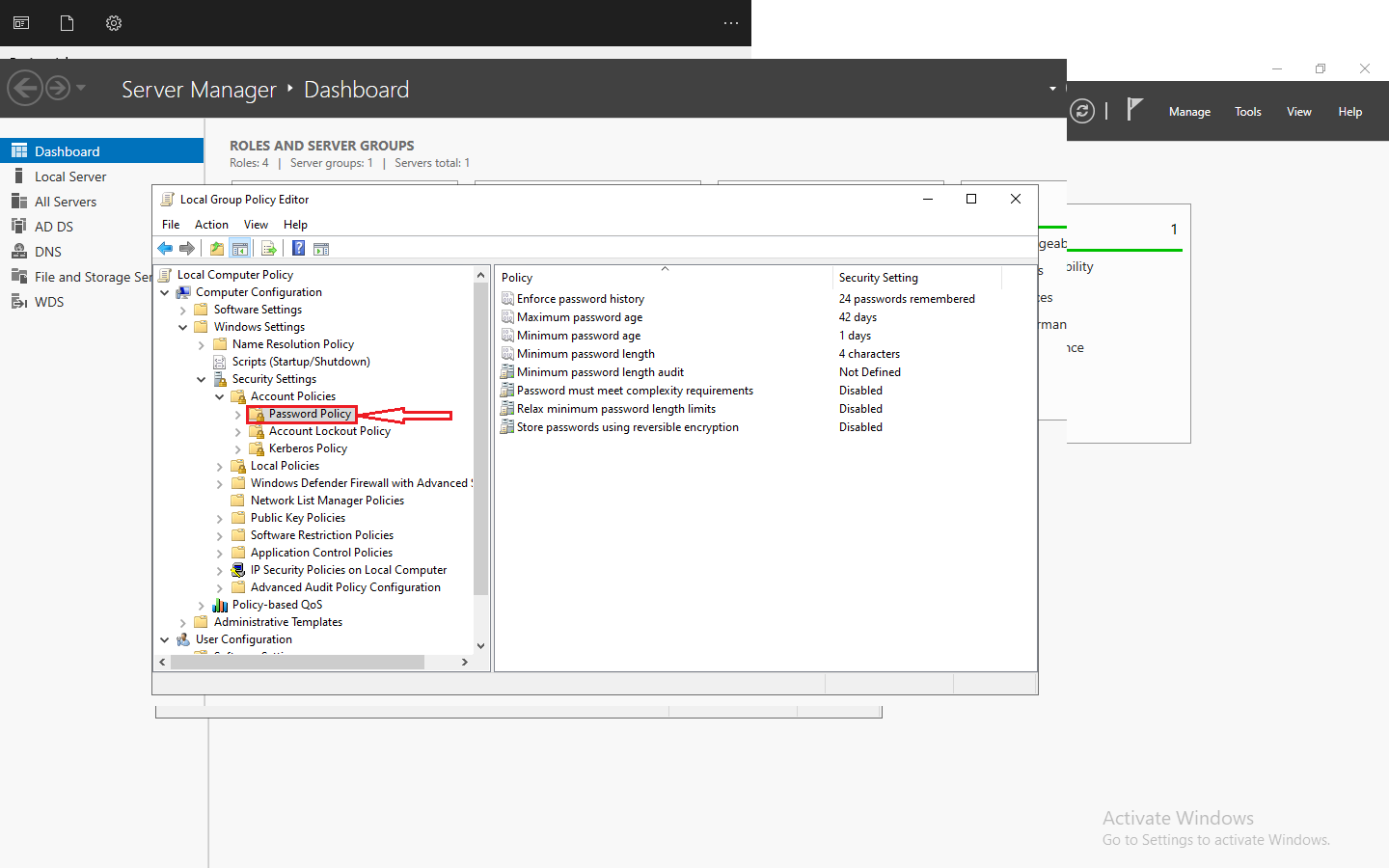
How Vmware vMotion Works
vMotion operates by generating a virtual machine duplicate on the target server, replicating the RAM and CPU state data from the source server, and promptly setting up network connections between the source and destination servers.When getting a VMware ESXi host ready for vMotion, various factors need consideration. These include:
Ensuring the CPU architecture is compatible between the source and target ESXi host.
Having access to the data stores where the virtual machine VMDKs are stored.
Using the same label for VMware Standard vSwitches (VSS) so that network connectivity is maintained when vMotioning a virtual machine.
Ensuring the physical network connections and labels are consistent across the ESXi hosts.
Having a minimum of a gigabit network connection. Enabling a vmkernel port with the vMotion service.
Challenges of Using VMware vMotion
Despite the numerous advantages offered by VMware vMotion, it’s crucial for business owners to be aware of certain drawbacks. One significant limitation is the necessity for a continuous connection between the source and destination servers. If this connection is disrupted, the migration may fail, resulting in the virtual machine being unable to sustain operation. Furthermore, the migration process itself can be time-consuming, potentially leading to unresponsiveness in the virtual machine and prolonging the overall migration duration.
Comparison of VMware vMotion and Storage vMotion
VMware vMotion and storage vMotion prove valuable in handling virtual environments, yet they differ in functionality. Despite sharing some similarities, these tools fundamentally serve distinct purposes, highlighting notable differences between them.
Similarities between VMware vMotion and Storage vMotion
The fundamental commonality between VMware vMotion and Storage vMotion lies in their shared purpose of overseeing components within a virtual environment. While VMware vMotion is utilized to relocate virtual machines (VMs) among physical servers, Storage vMotion is employed for the movement of virtual disks between different storage locations. Both technologies primarily enhance the efficiency of virtualization and minimize downtime during migration procedures. Another parallel aspect is their capacity to transfer VMs and associated data seamlessly without causing disruptions. This shared feature enables the smooth relocation of virtual machines and their data from one location to another, simplifying the management of virtual environments without interruptions.
Differences between VMware vMotion and Storage vMotion
The primary distinction between VMware vMotion and Storage vMotion lies in the nature of the data they transfer. While VMware vMotion relocates entire virtual machines (VMs) along with their associated elements, encompassing the operating system, applications, settings, and configurations, Storage vMotion specifically transfers the virtual disk linked to the VM. Another differentiating factor is the speed of data transfer; VMware vMotion is generally notably swifter than Storage vMotion. This is because Storage vMotion demands more time for the relocation of associated data. Furthermore, Storage vMotion is particularly effective when moving data exclusively between physical storage locations. Conversely, VMware vMotion demonstrates its capability by transferring entire VMs between physical servers.
Final Thought
VMware vMotion and Storage vMotion serve as robust tools facilitating the smooth and efficient transfer of workloads across diverse environments. VMware vMotion facilitates live migration of virtual machines and their associated data between distinct vSphere hosts. Simultaneously, Storage vMotion enables the dynamic relocation of virtual disks between different datastores.
These technologies play a crucial role in minimizing downtime, optimizing resource utilization, and ensuring peak performance for virtual workloads. Hence, when deciding between the two, it’s essential to evaluate the existing IT infrastructure, financial considerations, and the specific needs of your organization.